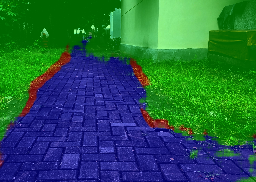
This project is a collaboration research with Active Intelligent System Laboratory, Toyohashi University of Technology, Japan. The goal is to detect and track an unstructured road boundary, mainly for robotic and intelligent vehicle navigation system. It has been done by Mr. Kazuki Mano under join supervision of Prof. Jun Miura and Dr. Igi Ardiyanto.
Arsip:
Projects
Discovering and drawing out the relationship between users and items in a service-based companies or organizations are the essence of a recommendation system. Here we address a novel approach for the recommendation system, incorporating the means of collaborative aspect between the users internal hidden patterns and the items or goods to be recommended. Unlike the existing methods, our algorithm introduces a guiding factor between the user hidden state and the choice over the item set, such that it gives additional degree of freedom for the recommendation system to opt on which factor is more prominent.
Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) is a disease which affect the vision ability. The observation by an ophthalmologist usually conducted by analyzing the retinal images of the patient which are marked by some DR features. However some misdiagnosis are usually found due to human error. Here, a deep learning-based low-cost embedded system is established to assist the doctor for grading the severity of the DR from the retinal images. A compact deep learning algorithm named Deep-DR-Net which fits on a small embedded board is afterwards proposed for such purposes. In the heart of Deep-DR-Net, a cascaded encoder-classifier network is arranged using residual style for ensuring the small model size. The usage of different types of convolutional layers subsequently guarantees the features richness of the network for differentiating the grade of the DR. Experimental results show the capability of the proposed system for detecting the existence as well as grading the severity of the DR symptomps.
I. Ardiyanto, H. A. Nugroho, R. L. B. Buana, “Deep Learning-based Diabetic Retinopathy Assessment on Embedded System”, The 39th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC 2017), pp. 1760-1763, Jeju Island, South Korea, 2017.
Road-scene segmentation is a part of general image segmentation problems which tries to characterize the road-scene and divides it into labeled area/objects, such as road, building, car, pedestrian, pavement, etc. This problem has a huge range of applications, e.g. Intelligent Vehicle and Advanced Driver Assistance System (ADAS). We develop RCC-Net, a deep learning-based algorithm for achieving a real-time road-scene segmentation for Advanced Driver Assistance System (ADAS). We have successfully built the RCC-Net on a low-cost embedded system, NVIDIA Jetson TK1, opening the possibilities for in-car deployment.
I. Ardiyanto, T.B. Adji, “Deep Residual Coalesced Convolutional Network for Efficient Semantic Road Segmentation”, IPSJ Transactions on Computer Vision and Applications (IPSJ-CVA), vol. 9:6, Springer, 2017. (Invited paper of MVA 2017, ISSN: 1882-6695)